Learning Outcomes:
i. Understand the concept of vector addition and its graphical representation.
ii. Apply the head-to-tail rule for adding vectors graphically.
iii. Recognize the commutative and associative properties of vector addition.
iv. Solve problems involving vector addition using graphical methods.
Introduction:
In the realm of physics, vectors are quantities that possess both magnitude and direction. Unlike scalars, which only have magnitude, vectors require both numerical and directional information to be fully described. Vector addition is a fundamental operation in physics, allowing us to combine multiple vectors to determine their resultant vector.
i. The Essence of Vector Addition
Vector addition is the process of combining two or more vectors to produce a single vector that represents the sum of their individual effects. Unlike scalar addition, where the order in which numbers are added does not matter, vector addition is not commutative. The order in which vectors are added can affect the direction of the resultant vector.
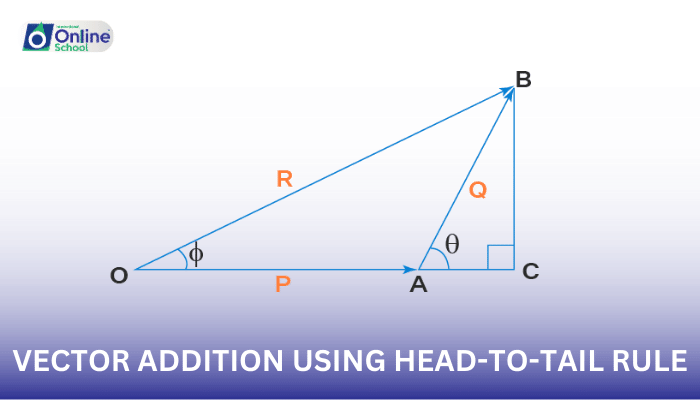
ii. The Head-to-Tail Rule: A Graphical Approach
A convenient method for visually representing vector addition is the head-to-tail rule. This technique involves placing the tail of the second vector at the head of the first vector, continuing this process for subsequent vectors. The resultant vector is then drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
Consider two vectors, A and B. To add them using the head-to-tail rule, follow these steps:
- Draw vector A on a coordinate plane.
- Place the tail of vector B at the head of vector A.
- Draw the resultant vector from the tail of A to the head of B.
- The resultant vector represents the sum of vectors A and B.
iii. Commutative and Associative Properties of Vector Addition
Vector addition possesses two important properties:
Commutativity: The order in which vectors are added does not affect the resultant vector. This means that
A + B = B + A.
Associativity: The grouping of vectors for addition does not affect the resultant vector. This means that
(A + B) + C = A + (B + C).
These properties simplify the process of vector addition and allow us to manipulate vector expressions without altering their outcome.
iv. Applying the Head-to-Tail Rule for Vector Addition
The head-to-tail rule can be applied to add multiple vectors. Simply follow the same process of placing the tail of each subsequent vector at the head of the previous vector, and draw the resultant vector from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
Vector addition is a fundamental concept in physics, and the head-to-tail rule provides a graphical method for visualizing and understanding this operation. The commutative and associative properties of vector addition further simplify vector manipulation and problem-solving.